Conveyors 101: A Beginner's Guide to Understanding Conveyors
11th Dec 2024
What is a Conveyor?
A conveyor is a mechanical system designed to transport materials efficiently, reliably, and safely across various distances. From cardboard boxes to wood, metal, or plastic containers, conveyors simplify material handling, reducing manual labor and increasing productivity in countless industries. Whether in manufacturing, warehousing, or logistics, understanding how conveyors work and their different types will help you identify the best solution for your business needs.
Types of Conveyors: From Basics to Specialized Systems
- Gravity Conveyors
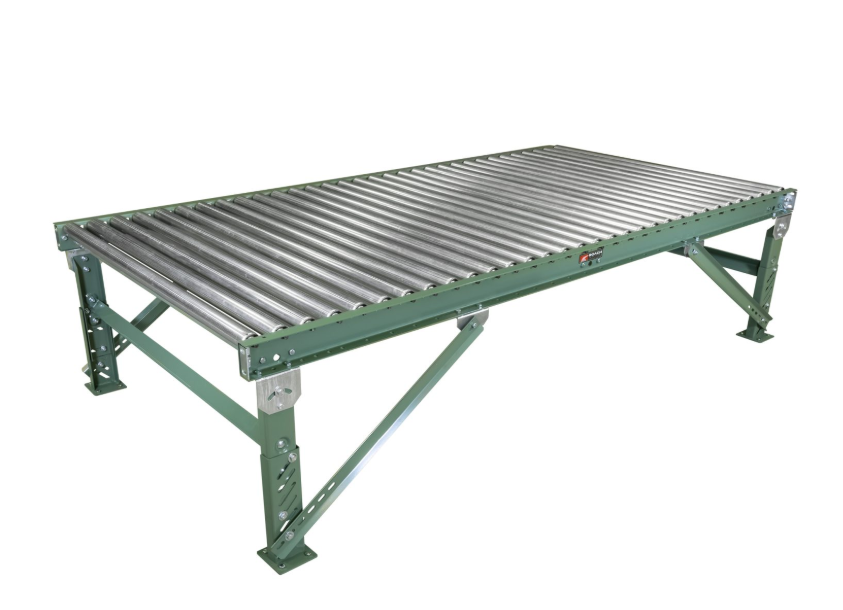

Gravity conveyors rely on the natural force of gravity to move materials. These systems are ideal for straightforward horizontal or inclined transport and require no power source, making them cost-effective and environmentally friendly. Typical applications include assembly lines and simple material transfer points.
- Belt Conveyors
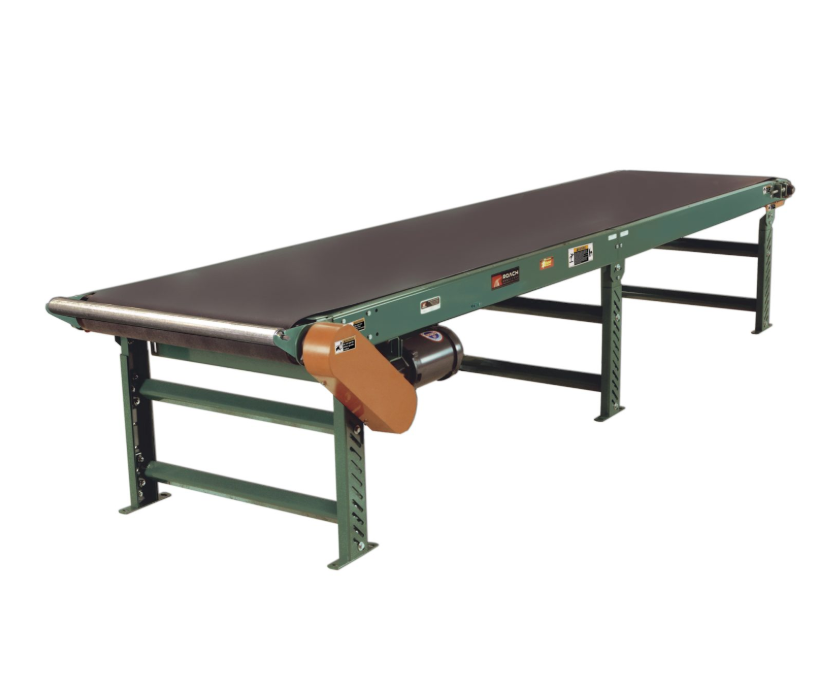

Belt conveyors use an endless belt driven by an electric motor to move materials horizontally or on an incline. These systems are versatile and can handle a variety of materials, from lightweight items to heavier loads. Key components include:
- Bed and Pulley System: The belt rests on a flat or roller-supported bed, guided by drive and tail pulleys.
- Bearings and Idlers: Bearings reduce friction, while idlers support the belt for smooth motion.
- Motors and Speed Reducers: Electric motors drive the belt, and speed reducers control the pace, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
- Roller Conveyors
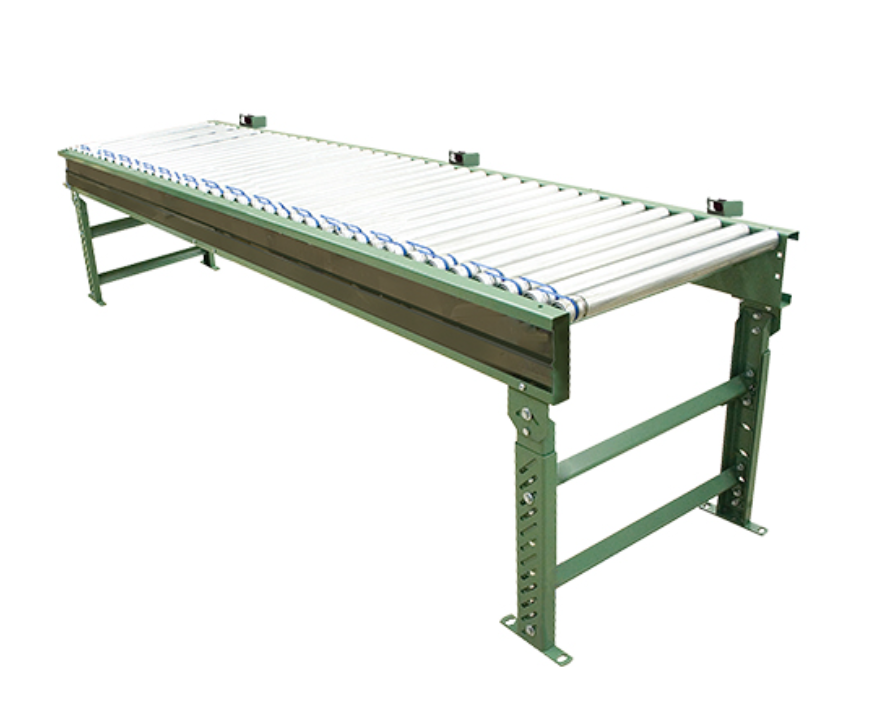

Roller conveyors use cylindrical rollers to transport materials. These systems are well-suited for heavier or uneven loads and offer low friction, making them energy-efficient. Variants include:
- Skate Wheel Conveyors: Perfect for lightweight, flat-bottomed items like boxes or trays.
- Accumulating Conveyors: These can hold items temporarily with adjustable pressure to prevent damage, which is ideal for buffering and sorting.
- Incline Conveyors
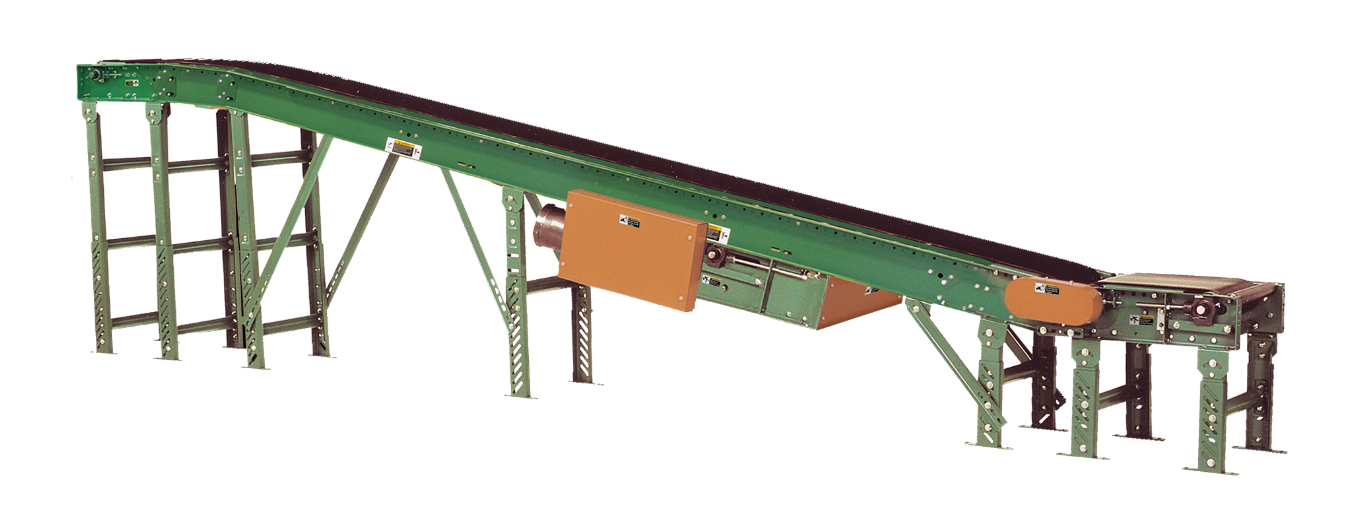

Incline conveyors are designed to move materials uphill, often including a power feeder to ensure smooth transitions between levels. Typically capped at a 30-degree incline, these systems prevent material slippage. Typical applications include mezzanine transport and stacking operations.
- Live Roller Conveyors
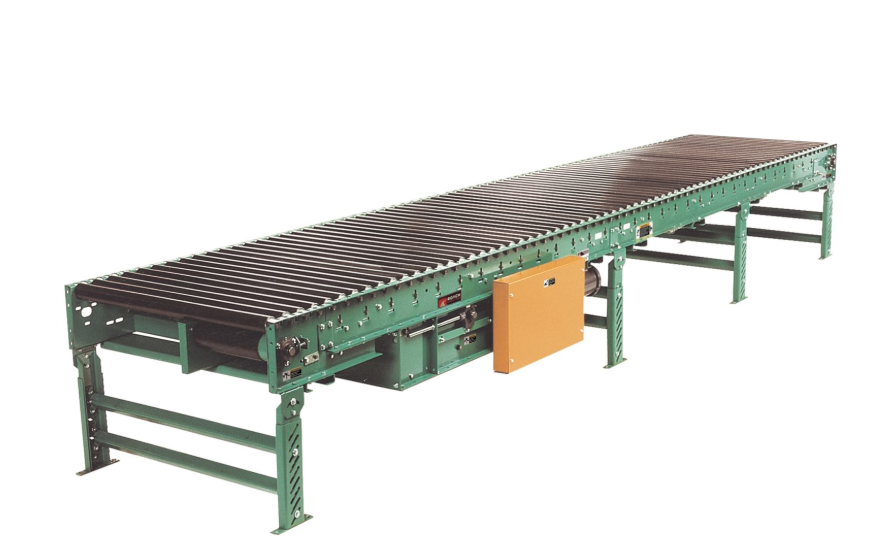

Powered by belts or chains, live roller conveyors offer precision control for transferring materials between systems. Operators can start, stop, or momentarily hold items for tasks such as labeling, inspection, or sorting.
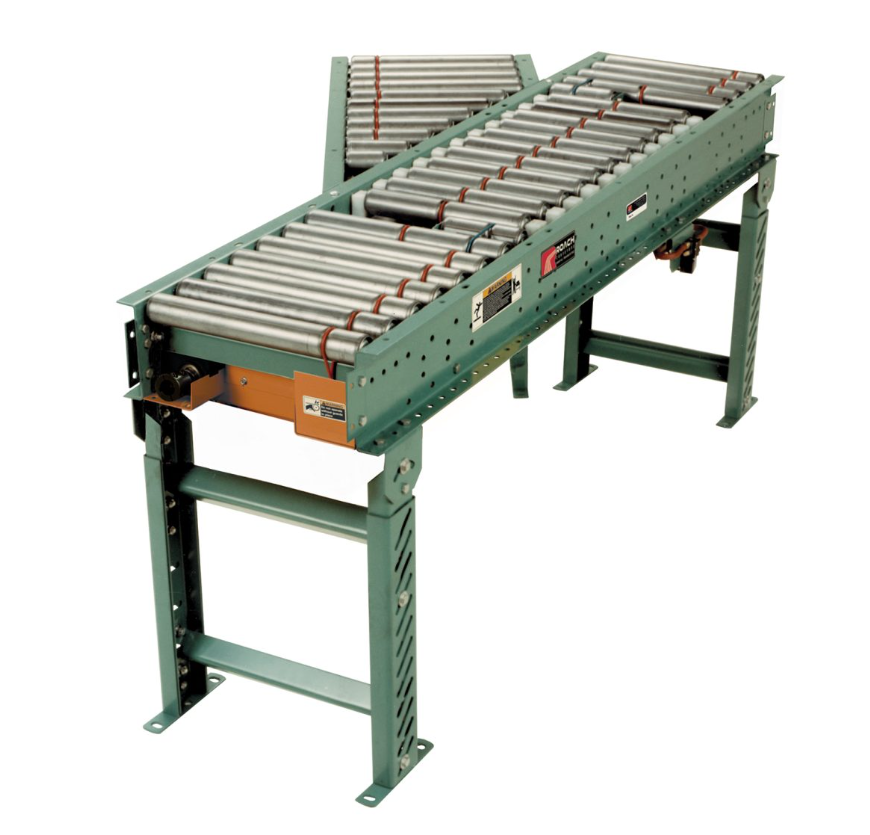
Picture of a Parts Conveyor:

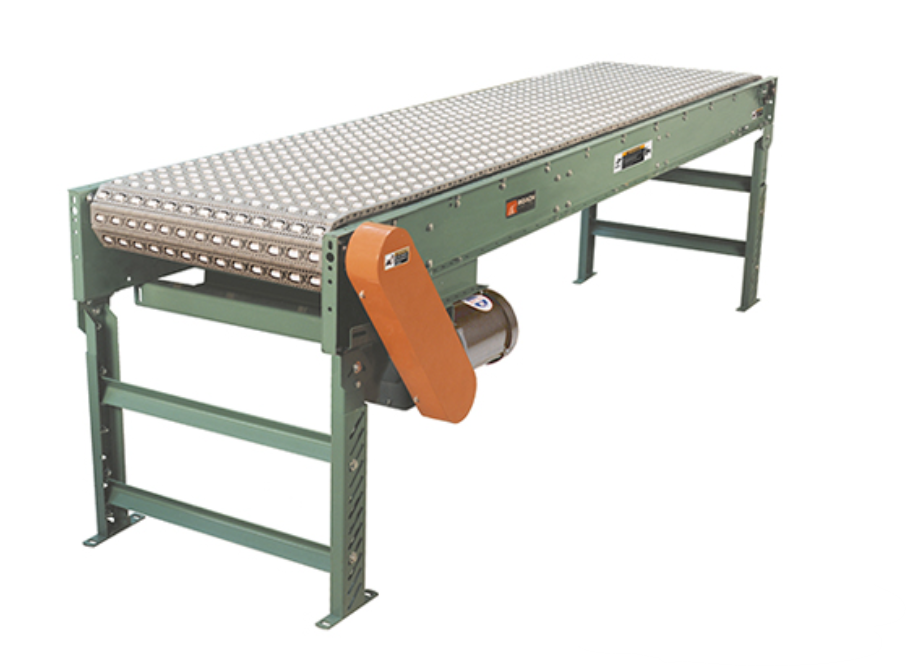
Picture of a Plastic Belt Conveyor:

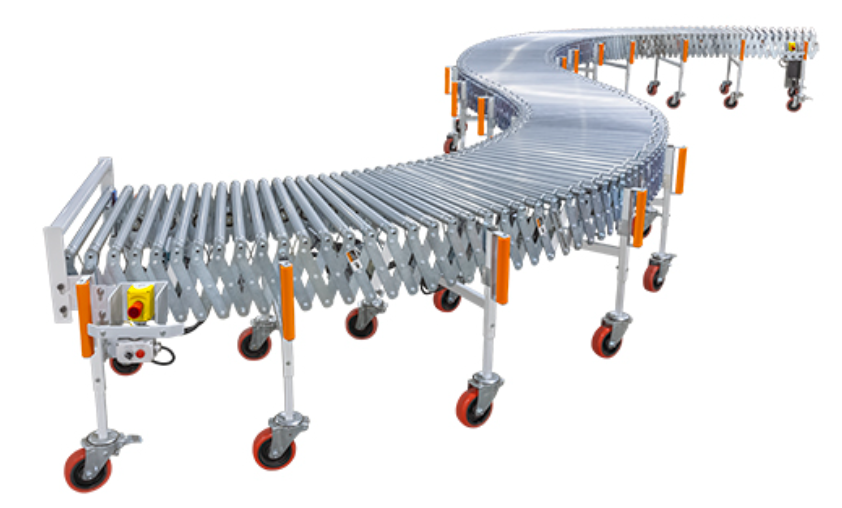
Picture of a Flexible Conveyor:

Key Features and Components of Conveyor Systems
Belting Materials
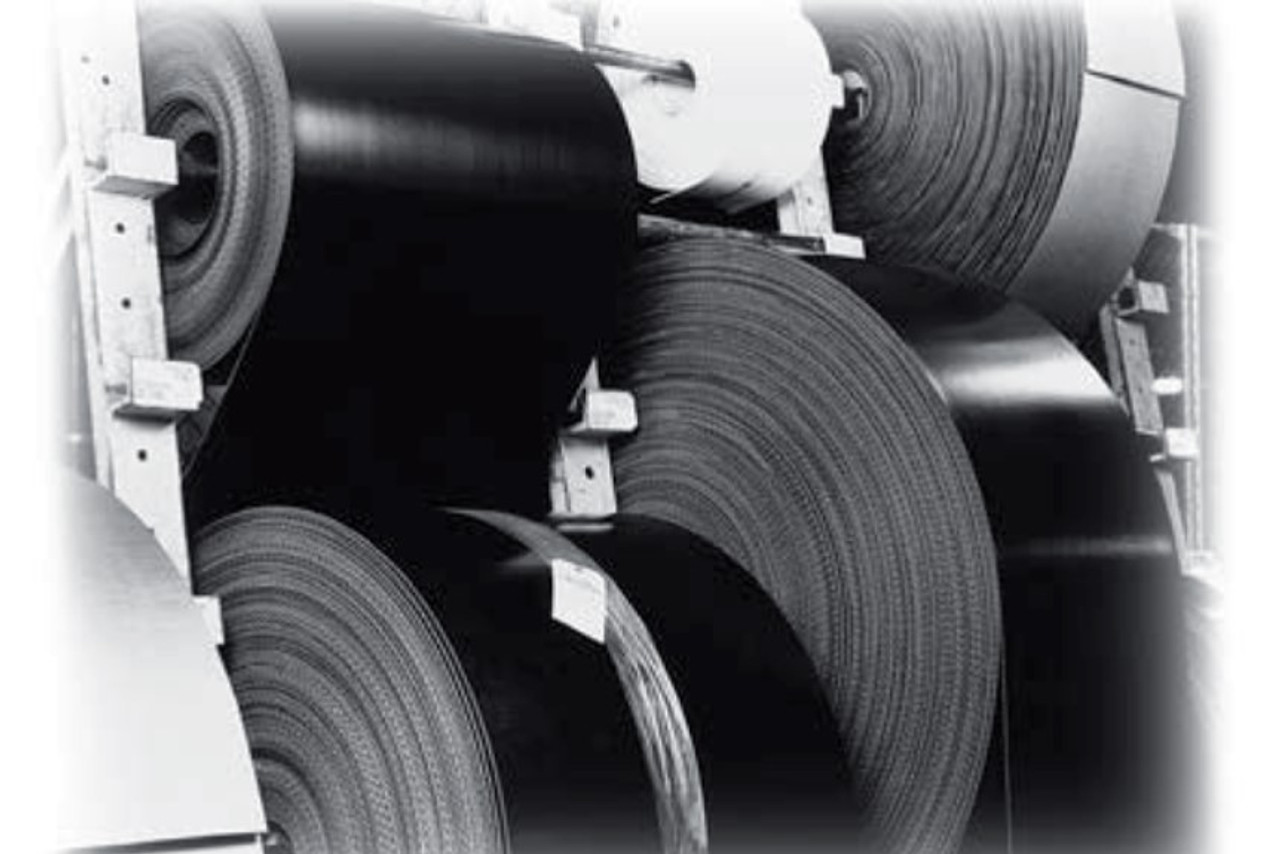

Conveyor belts are tailored to specific operational conditions:
- PVC Belts: Offer oil and chemical resistance.
- Rubber Belts: Provide excellent grip for materials on inclines.
- Teflon Belts: Ideal for sticky or heat-sensitive materials.
Guard Rails and Safety Features
To enhance safety, guard rails prevent materials from falling off the conveyor, while emergency stop switches and protective covers minimize operator risk.
Switches and Diverters
- Spur Switches: Direct materials onto different lanes.
- Pop-Up Wheel Diverters: Handle high-speed sorting, rapidly moving up to 40 items per minute.
Spur Switch Example: Roach 796LSS shown

Customizing Your Conveyor System
Hybrid Flow Systems
A flow system combines gravity and powered conveyors, offering seamless transitions and optimized material flow. These systems can be customized to match unique business processes and layouts.
Environmental Considerations
Dust, moisture, heat, or cold can influence conveyor selection. Durable materials, specialized coatings, and sealed bearings ensure reliability in harsh environments.
Load Requirements
The transported materials' weight, size, and shape dictate conveyor design. Heavy-duty construction, reinforced bearings, and cleated belts can efficiently handle demanding loads.
Electrical Controls
Advanced electrical controls enhance automation and safety. Options include:
- Manual Switches: For basic on/off functionality.
- Photoelectric Sensors: For hands-free operation and material tracking.
- Magnetic Starters: Protect against overload and ensure consistent performance.
Advanced Features for Efficiency and Longevity
High-Speed Capabilities
Modern conveyors feature rapid sorting mechanisms, precisely handling up to 40 items per minute.
Specialized Belts
- Wire Mesh Belts: Resist extreme temperatures in applications such as baking or cooling.
- Cleated Belts: Secure materials during steep inclines or declines.
Durability Enhancements
Reinforced frames, high-performance seals, and anti-corrosion coatings extend the lifespan of your conveyor system, ensuring a solid return on investment.
Building the Perfect Conveyor System
Whether you're looking for a simple gravity conveyor or a fully automated flow system, the right solution can streamline your operations, reduce costs, and improve overall productivity. At Material Flow, we specialize in custom conveyor solutions tailored to your unique business needs.
Our expert team is ready to help you design, build, and implement the ideal conveyor system for your operation. Contact us today to get started and elevate your material handling efficiency!